티스토리 뷰
11.2 Basic ideas
Morphology (형태) : a branch of image processing which is useful for analysis shapes in (binary) images
1) Translation
A : a set of pixels in a binary img
w = (x, y) : a particular coordinate point
A_w = { (a, b) + (x, y) : (a, b) ∈ A} : a set A 'translated' in direction (x, y)

(Matrix coordinate : The origin is at the top left → x goes down, y goes across)
2) Reflection
A^ = { (-x, -y) : (x, y) ∈ A} : a set obtained by reflecting A in the origin

11.3 Basic operations : Dilation and Erosion
All operations are built from a combination of Dilation and Erosion
1) Dilation (팽창)
A : img being processed
B : a small set of pixels (= a structuring element of a kernel)
Dilation of A by B : Union of all translations of A by every point x ∈ B
⇔ replacing every point (x, y) in A with a copy of B
Effect : thickening the img or increasing the size of object (if only the original object A lies within its dilation)




>> imdilate(image,kernel)>> t = imread('text.jpg');
>> sq = ones(3,3);
>> td = imdilate(t,sq);
>> subplot(1,2,1), imshow(t)
>> subplot(1,2,2), imshow(td)
2) Erosion (침식)
Erosion of A by B
: move B over A and find all places it will fit → mark down the corresponding (0, 0) point of B
If B contains the origin, then erosion will be a subset of the original object
Effect : thinning the img
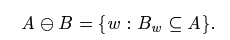

>> imerode(image, kernel)>> c = imread('text.jpg');
>> sq = ones(3,3);
>> ce = imerode(c, sq);
>> subplot(1,2,1), imshow(c)
>> subplot(1,2,2), imshow(ce)
Relationship bw erosion and dilation
They are Inverse of each other
⇔ The complement of erosion = dilation of the complement


Application : Bounary Detection
A : an img
B : a small structuring element consisting of point symmetrically places about the origin
The boundary of A :

>> rice = imread('rice.jpg');
>> rice = rgb2gray(rice);
>> r = rice > 110;
>> sq = ones(3,3);
>> re = imerode(r, sq);
>> r_int = r & ~re;
>> subplot(1,2,1), imshow(r)
>> subplot(1,2,2), imshow(r_int);
>> rd = imdilate(r, sq);
>> r_ext = rd & ~r;
>> r_grad = rd & ~re;
>> subplot(1,2,1), imshow(r_ext)
>> subplot(1,2,2), imshow(r_grad)
11.4 Second level operations : Opening and Closing
1) Opening
Opening of A by B
: a erosion followed by a dilation (erosion → dilation)
⇔ union of all translation of B which fit inside A


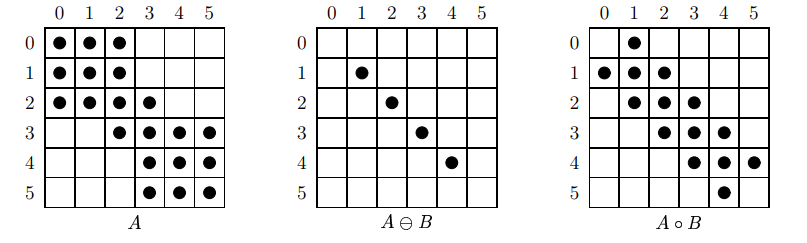
Properties of opening operation

2) Closing
: a dilation followed by a erosion (dilation → erosion)
⇔ all translations B_w which contain x have nin-empty intersections with A


Properties of closing operation


Relationship bw opening and closing
Complement of an opening = closing of a complement
Complement of an closing = opening of a complement
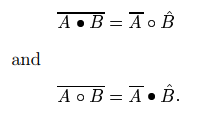
Application : Noise Removal
A : a binary img corrupted by impulse noise
Morphological filtering : Noise Removal method by opening followed by closing (opening → closing)
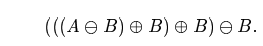

>> c = imread('rice.jpg');
>> c = rgb2gray(c);
>> x=rand(size(c));
>> d1=find(x<=0.05);
>> d2=find(x>=0.95);
>> c(d1)=0;
>> c(d2)=1;
>> sq = [1 1 1 ; 1 1 1 ; 1 1 1];
>> cr = [0 1 0 ; 1 1 1 ; 0 1 0];
>> cf1=imclose(imopen(c,sq),sq);
>> cf2=imclose(imopen(c,cr),cr);
>> subplot(1,3,1), imshow(c)
>> subplot(1,3,2), imshow(cf1)
>> subplot(1,3,3), imshow(cf2)
11.5 The hit-or-miss transform

Ex. Text eroded by a hyphen-shaped structuring element
find the hyphen in 'cross-correlation' in the text img (6 lines)
>> b1=ones(1,6);
>> b2=[1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1;1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1; 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1];
>> tb1=erode(t,b1);
>> tb2=erode(~t,b2);
>> hit_or_miss=tb1&tb2;
>> [x,y]=find(hit_or_miss==1)
>> figure, plot(tb1)
11.6 Some morphological algorithms
1) Region filling

2) Connected components

3) Skeletonization
Skeleton : medial axis transform

'DIP > Matlab' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Ch12] Color Processing (0) | 2023.01.09 |
|---|---|
| [Ch10] The Hough and Distance Transform (0) | 2023.01.09 |
| [Ch9] The Fourier Transform (0) | 2022.03.06 |
| [Ch8] Edges (0) | 2022.02.20 |
| [Ch7] Noise (0) | 2022.02.12 |
